20241229 – Sentience

MAIN IDEA:
This book is about conscience, sentience, the relationship between these two notions, and the evolutionary meaning of their development. The author defines these notions thus:
“The adjective ‘sentient’ came into use in the early seventeenth century to describe any creature—human or otherwise—that responds to sensory stimuli. But the meaning subsequently narrowed to put emphasis on the inner quality of the experience: what sensations feel like to the subject.”
“Consciousness means having knowledge of what’s in your mind. Your conscious mental states comprise just those states to which at any one time you have introspective access and of which you are the subject.”
After that, the author presents the results of the research on monkeys with different parts of the brain disabled and some unexpected results that it produced. The author also discusses sensations and perceptions using such framework:” “Sensations are about what’s happening to you at your sense organs. Perceptions are about the state of the world.”
Finally, the author allocates much space to discussing non-human sentience and conscience. Eventually, he concludes:” While we needn’t doubt that there are many other life forms out there in the universe, we’ve come to see that the evolution of life, even intelligent life, will not necessarily have entailed the evolution of phenomenal consciousness. On Earth, it has so happened that a sequence of ‘lucky’ breaks paved the way for it to evolve as it has done in mammals and birds. On Earth, if the same local conditions were to hold, it’s quite possible that the sequence could be repeated. But outside the Earthly environment all bets are off. The chances of phenomenal consciousness having evolved somewhere else in the universe could be vanishingly small.

MY TAKE ON IT:
I think that sentience is a common feature of any object, whether living creatures or automata, capable of changing its condition in time and space due to interacting with the surrounding environment to achieve whatever objective this object has. Obviously, a more complex system, especially if it is biological, possesses much more complex internals and, therefore, has less predictability of change in internal conditions in response to stimuli. At some point, these internals include conscience as a tool that allows individuals to cooperate with others at high levels of sophistication and to handle a rapidly changing environment with success impossible at the lower levels. A big part of this cooperation is a highly developed language that allows conscientious creatures not just to transfer complex information but also to save it in distributed form so a group can do something that nobody can do alone. Moreover, it allows intergenerational cumulative transfer, leading to eventual progress in dealing with the environment from generation to generation. In other words, expanding sentience into conscience is not inevitable, but if it happens, it provides a huge evolutionary advantage.
20241222 – Theory of Irregular War

MAIN IDEA:
This book is about a specific way of conducting a war, and here is how the author defines the general meaning of war:” Whether those ways are conventional/unconventional, regular/irregular, symmetric/asymmetric, overt/covert, Napoleonic/Fabian, or any other diametric word pairing is irrelevant at the level of analysis dealing with war itself. War is a sovereign weapon expressed through organized violence between parties clashing over incommensurable policies.”. The author defines the objective of the book this way:” This book will accomplish two things: I will show that existing theoretical frameworks are insufficient to understand and explain irregular wars and I will present a novel theory that can. To do so, let us begin with a technical definition of irregular war. Irregular war is the apotheosis of conflict between the people and the state, a violent dialectic between a faction and a sovereign expressed outside existing political institutions.
The author nicely summarizes his theory in a few graphic representations:
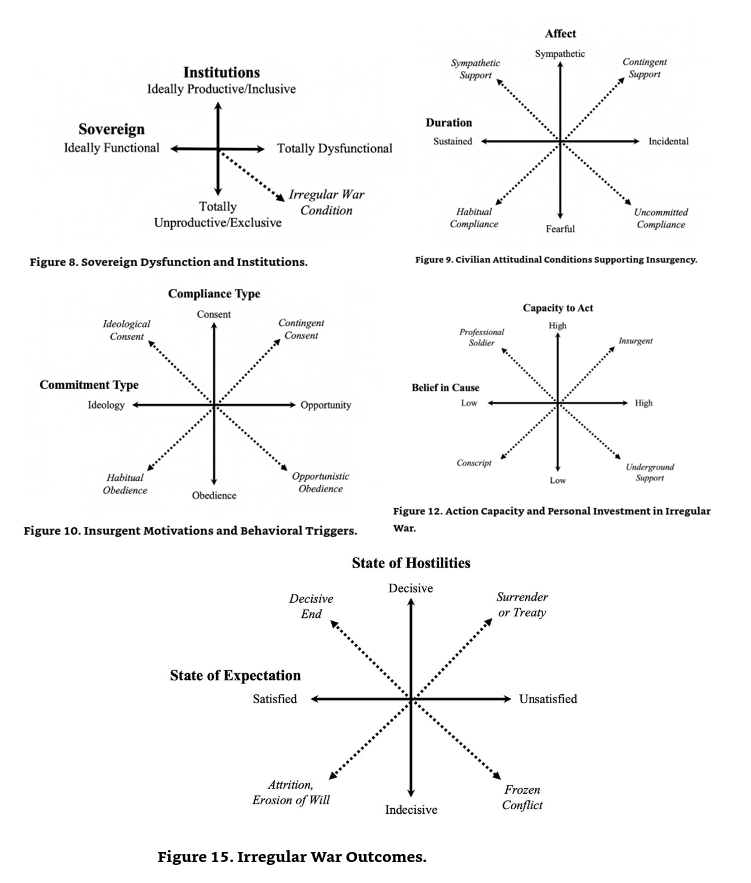

MY TAKE ON IT:
The author based the discussion of this book mainly on examples of colonial wars, such as the French in Algiers, or wars of external support for unpopular regimes, such as the American war in Vietnam. I think the author underestimates the role of external support for the irregular side of the war. There would be no serious resistance in Algiers or Vietnam without Soviet and Chinese support, which provided resources and save heavens for regrouping, rest, and resupply. When such support was weak or nonexistent, as was the case for Ukrainian and Baltic states’ resistance against the Soviet Union, the colonial power always won, even if it took a few years. The problem was that the Western powers tended to overcomplicate situations and overly rely on pseudo-expert opinion (pseudo because these “experts” often did not even know the local languages). Most importantly, they typically defined unrealistic objectives and tried to fit reality into the rigid framework, either turning Algier into France despite the huge cultural gap between populations or winning the hearts and minds of Muslim tribesmen in Afghanistan for American-style democracy. The realistic objective would be to eradicate whoever supports hostile, terroristic actions as quickly as possible and get out. If, after that, terrorist activities resume, come back, repeat, and get out. After a few repetitions, the normal evolutionary process would work out, leaving in place peaceful survivors who hate the very idea of terrorism and its inevitable consequences. There should be no attempts to impose on people values that are not acceptable to them, such as Western civilizational values of individual freedom and democracy.
20241215 Ranganath, Charan – Why We Remember

MAIN IDEA:
This is the look at memory from the point of view of human evolution. The author’s main point is that memory is nothing like computer memory with write/read features, albeit not as reliable and photographic. Here are the two most important author’s definitions:
- Memory is much, much more than an archive of the past; it is the prism through which we see ourselves, others, and the world. It’s the connective tissue underlying what we say, think, and do.
- We forget because we need to prioritize what is important so we can rapidly deploy that information when we need it. Our memories are malleable and sometimes inaccurate because our brains were designed to navigate a world that is constantly changing: A place that was once a prime foraging site might now be a barren wasteland. A person we once trusted might turn out to pose a threat. Human memory needed to be flexible and to adapt to context more than it needed to be static and photographically accurate.
The author also provides an excellent technical description:” I think of memory as the process by which our brains change over time. As we go about our lives, connections between neurons are constantly formed and modified, resulting in cell assemblies that help us sense, interact with, and understand the world around us. These intricately connected neural networks give us the ability to weave together the threads of the past so that we may envision how the future will unfold.”

MY TAKE ON IT:
I fully agree with the author that human memory has developed as an effective tool for survival and, as such, provides not an accurate picture of the past but rather a presentation of reality compiled from a combination of previous presentations and current inputs from both the external environment and the body’s internal conditions. This presentation serves one and only one purpose: to prompt such action or inaction that in the past was beneficial for survival and procreation. For conscientious beings such as humans, memory defines the notion of self and where this self belongs in relation to other selves and within the universe.
From this, I’d like to draw the important conclusion that we cannot rely on human memory in many important areas, from witness evidence to a view of past events and interactions.
Luckily, we have technology that allows us to save audio and visual information in just about any conceivable circumstance, and this technology improves constantly. So, any review and analysis of past events, whether a crime or who said and did what and where, should be based not on witness evidence but on technical recordings. However, it also contains the danger of modifying the recording using AI. The only way it could be prevented is by continuing blockchain postings of everything from everybody. It would be absolutely inconceivable back in the 1970s when we saved 2 bytes on a timestamp of the year, but it is conceivable now when we can carry terabytes of data on keychains in our pockets.
20241208 Khan, Salman -Brave New Words

MAIN IDEA:
This book presents some of Khan Academy’s history, but it is mainly about how the AI tool ChatGPT is used to improve its online courses. Based on this experience, the author defines the opportunity provided in this way:” What might it be like if every student on the planet had access to an artificially intelligent personal tutor: an AI capable of writing alongside the student; an AI that students could debate any topic with; an AI that fine-tuned a student’s inherent strengths and augmented any gaps in learning; an AI that engaged students in new and powerful ways of understanding science, technology, engineering, and mathematics; an AI that gave students new ways of experiencing art and unlocking their own creativity; an AI that allowed for students to engage with history and literature like never before?”
The author clearly understands that the old structure of labor and management as a pyramid is going away due to the automatization of everything everywhere with AI tools and envisions a solution in reforming education:” The real solution is to invert that labor pyramid so that most people can operate at the top and use AI and other technology for their own productivity and entrepreneurship. The only way we have a hope of doing this is to use the same AI technology to lift the skills of a large chunk of humanity in the coming decades.”

MY TAKE ON IT:
This is a very good report from the trenches of the fight for real education vs indoctrination. The author is absolutely correct that only switching to an AI-supported education process could provide the knowledge and skills necessary to maintain competitiveness in the labor market. However, if one rises above the narrow field of education and looks at the bigger picture of the economy, it would be obvious that the very need for human labor becomes obsolete, similar to the need for animal muscles for transportation. All human activities necessary to produce goods and services will become automated within the next 50 to 100 years because no human can compete with machines in producing goods and services, regardless of how complicated the production process is. So, the objective of education should switch from molding human beings who are good, reliable, and effective pieces of business or government hierarchy into individuals possessing the knowledge and skills necessary for self-fulfillment and the pursuit of happiness. It does not mean there will be nothing to do for individuals with scientific curiosity or entrepreneurial drive. It just means that such people will be able to satisfy their needs without other people spending their lives doing soul-killing routine jobs. Just imagine Henry Ford without the need for assembly line workers and engineers because AI-controlled automated tools can not only manufacture cars but also design these cars and do everything else necessary. In this case, we can have a wide variety of ideas for transportation that could be analyzed and processed in cyberspace, with actual production implemented only as needed. Obviously, it will require restructuring of society’s organization and resource allocation, which I believe will move in the direction of increasing individual freedoms via the expansion of private property in such a way that it would be available to everybody without diminishing rewards for the individuals most effective in creating something that other people need.
20241201 – A Theory of Everyone

MAIN IDEA:
The author claims that humans generally poorly understand themselves and their environment, analogous to fish that do not know what water is. So, here is the general description of the book per author:” This book is about the species called Homo sapiens…. From ancient bacteria-like life forms, humans have evolved through various laws that we shall explore in this book. But the forces that shape our thinking, our economies, and our societies have become invisible to us. And this leaves us with a deep, potentially existential problem. If we do not know who we are and how we got here, we cannot choose where we go next. If we cannot perceive the forces that shape us, we are impotent to shape these forces.”
Correspondingly, the author’s objective is to suggest what to do next:” It is about the future of humanity; about how each of our actions contributes to a collective brain. It’s about how Homo sapiens can reach the next level of abundance that leads to a better life for everyone and perhaps one day a civilization that spans the galaxy. And it’s about the things that stand in the way of getting where we need to be and what we can do to overcome them. Because today we stand on the shore of a sea of possibilities. We must be careful in how we address the coming waves ahead of us; waves that threaten our now precarious fossil-fueled civilizations.”
Here Is a nice graph presenting the author’s understanding of humanity:
The author concludes with this:” I hope this book has provided tools for how to advocate and what to advocate for. Not proximate solutions that patch problems and polarize groups, creating more problems, but instead permanent systematic ultimate solutions. I hope I have helped you realize that our problems and their answers don’t lie with any particular leader, any particular person, or any particular group. They require us to consider the rules of the system and what they inevitably lead to. Often, we cannot design the right rules, but we can create conditions for the right rules to evolve.
We have laws of life and a theory of everyone. We have a periodic table for people.
I hope you now know the answer to what Wallace’s older fish asked. I hope you can now see the water. We have the power to shape our societies, to influence our systems, and to determine our future. We can crack the next energy revolution to create a world that is not just sustainable, but thriving; not just efficient, but just; not just innovative, but transformative. The laws of life will go ever onwards. If we make the right decisions, so too will we”.
CONTENT:

MY TAKE ON IT:
I agree with the author’s characterization of humanity, except for the idea of the “collective brain.” I think that the most harmful mistake in human thinking is the neglect of human individuality and the attempt to simplify humans by grouping them into cultural, ethnic, religious, and other groups. In reality, every human being could be represented by a multidimensional Venn diagram of genotypic and phenotypic features changing dynamically and unpredictably. Technological development makes all humans increasingly powerful, so the only way to prevent using this power against others is to ensure maximal freedom of individuals supported by resource availability and combined with the strict cultural upbringing that makes any attempt to force one’s own will on others psychologically impossible. It is also necessary to ensure the development of such attitudes to interhuman interactions that any attempt to do so would prompt resistance. In other words, we should move as close as possible to the psychological environment consistent with humanity’s background as hunter-gatherers when resources are available to everybody more or less equally, cooperation is voluntary, and leadership is based on competence rather than some formal hierarchical structure. Since different people are competent in various areas, the leadership would be fluid depending on which area requires cooperative efforts. I would guess that with the development of AI tools, the need for cooperation in the way when one individual must be a tool for achieving the objectives of another, such as a general/soldier or an entrepreneur/hired hand, will be diminished all the way to non-existence. In this case, voluntary cooperation would be directed mainly at achieving happiness via interaction rather than survival via sacrifice.
